How To Calculate Vapor Pressure Lowering
1 p s o l u t i o n x s o l v e n t p s o l v e n t o.

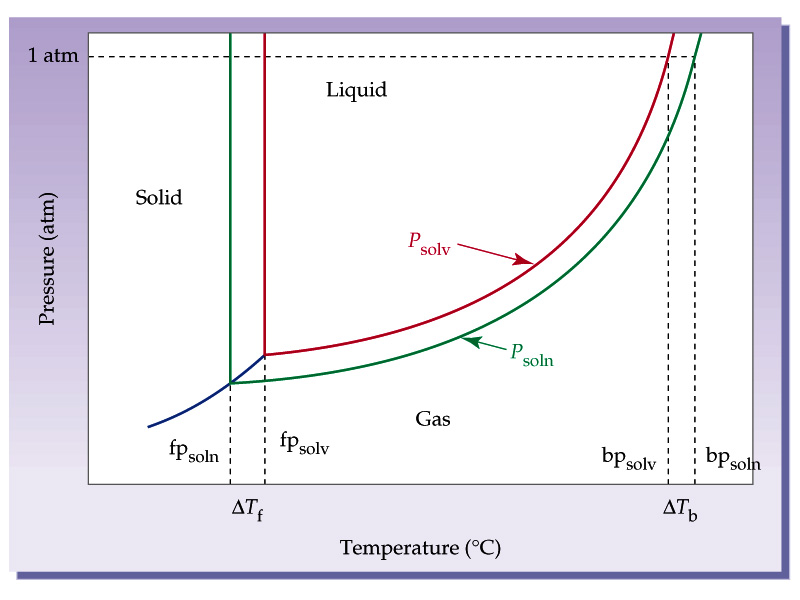
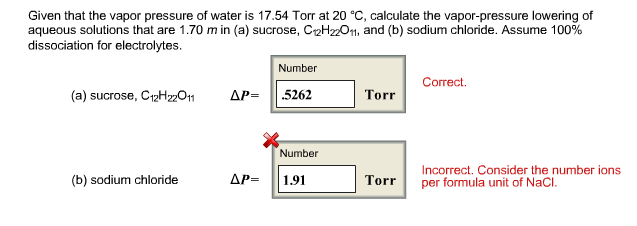
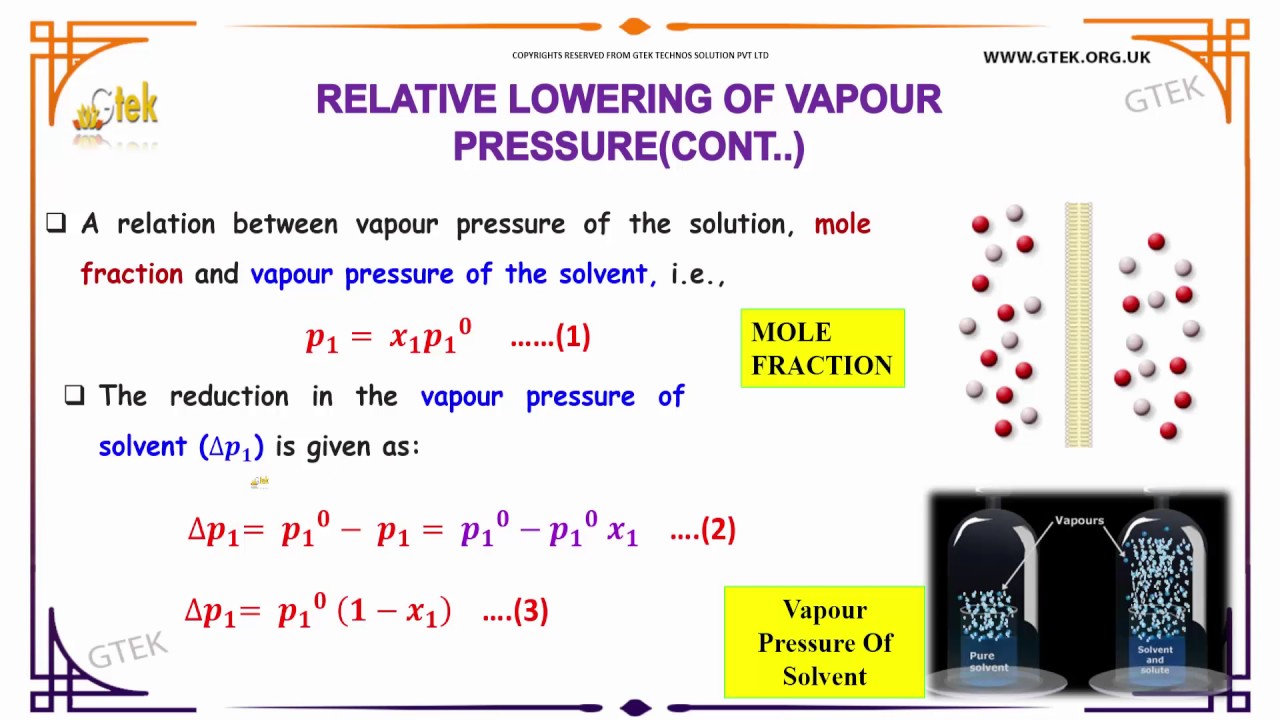
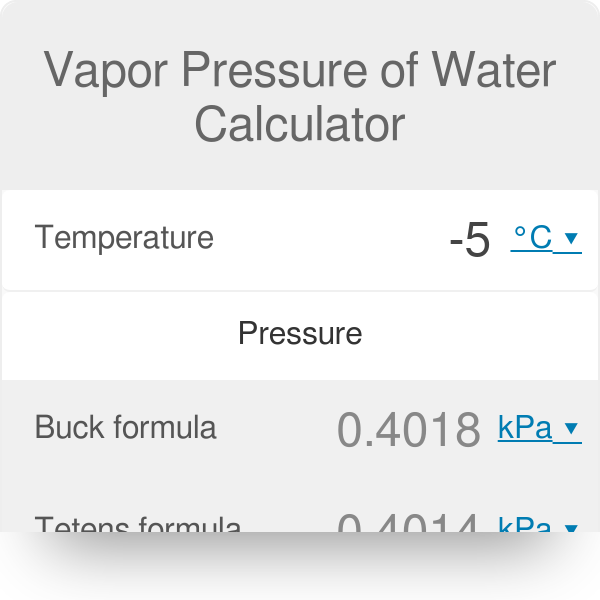
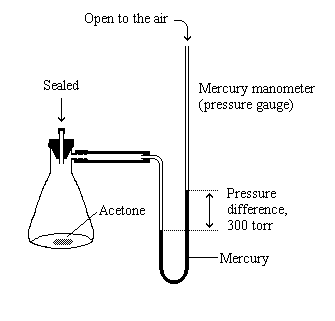
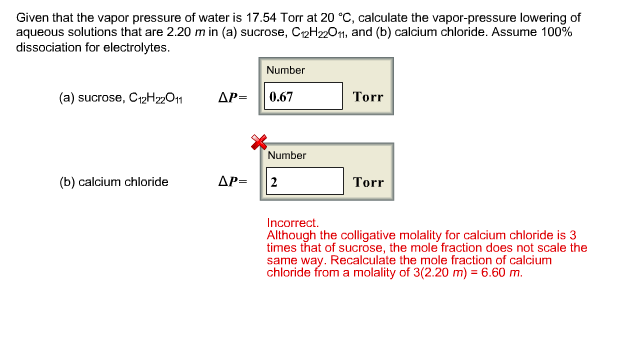
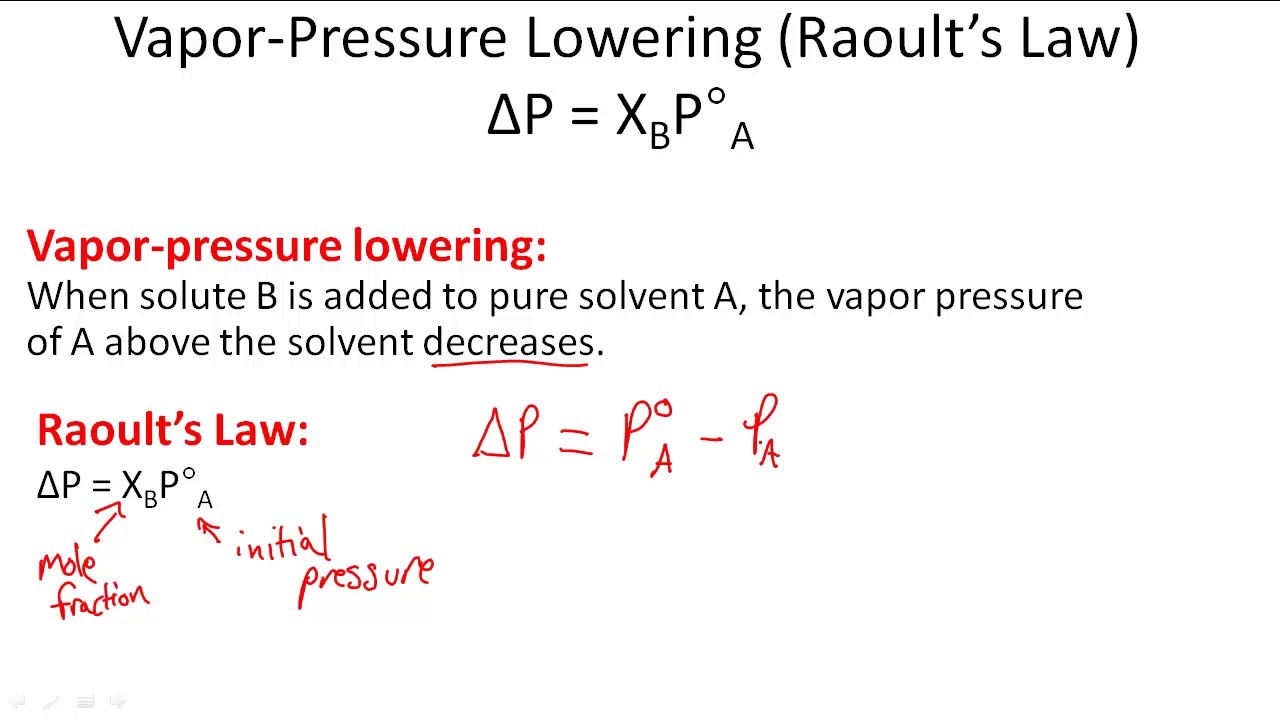
How to calculate vapor pressure lowering. This is raoults law. The vapor pressure of a solvent in a solution is always lower than the vapor pressure of the pure solvent. 2376 ps 2376 x 2 x 00641 3046. In chemistry vapor pressure is the pressure that is exerted on the walls of a sealed container when a substance in it evaporates converts to a gas.
The vapor pressure lowering is directly proportional to the mole fraction of the solute. Thus you have x wat 14 025 x eth 24 05 and x ace 14 025. So vapor pressure of solution 20714. Ln p1p2 dhvapr 1t2 1t1.
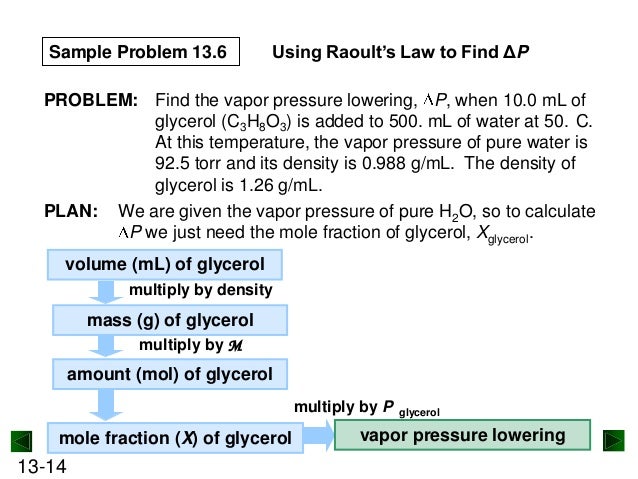
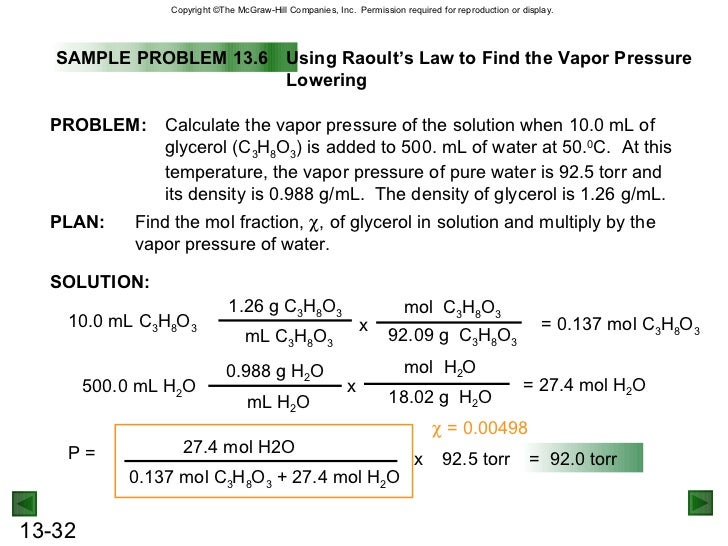
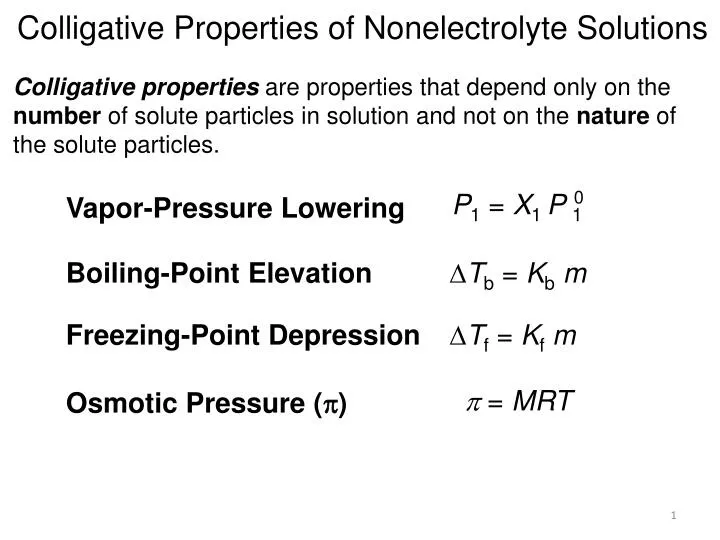
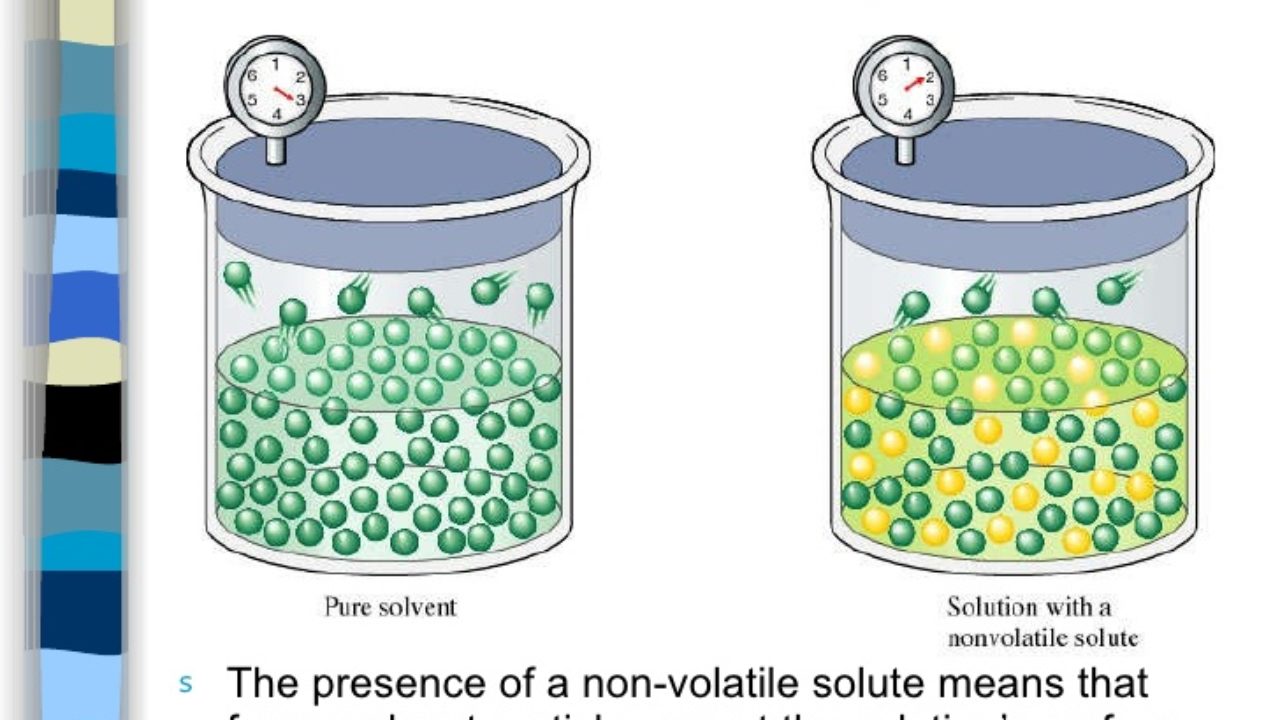
Raoults law relates the vapor pressure of a solution on the mole fraction of the solute added to a chemical solution. We need two pieces of information to calculate the reduction of the vapor pressure of the solvent in a solution containing a nonvolatile nonelectrolyte. When xsolvent 1 solutes present psolvent posolventie the vapor pressure of the solvent above the solution is lowerthan the vapor pressure above the pure solvent. Simplepressure e20386 5132 temperature 273 where vapor pressure is expressed in mmhgand temperature in kelvins.
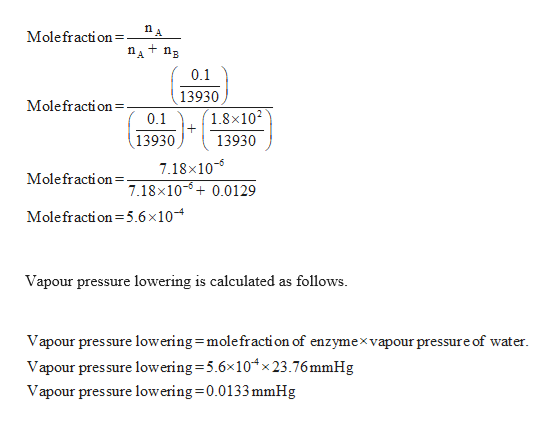
The mole fractions of the respective substances are the number of moles of each divided by the total moles of substance in the solution which is 1 2 1 4. Recall that the vapor pressure of a liquid is determined by how easily its molecules are able to escape the surface of the liquid and enter the gaseous phase. When xsolvent 1 pure solvent psolvent posolvent and. X2 25840263 00641.
P total p wat x wat p eth x eth p ace x ace. A colligative property is a property of a solution that depends only on the number of solute particles dissolved in the solution and not on their identity. 2376 ps 2376 2 x 00641. The mole fraction of the nonvolatile solute x solute in the solution.
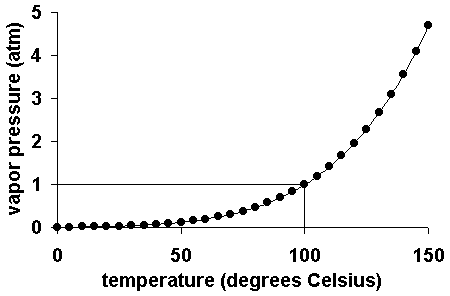
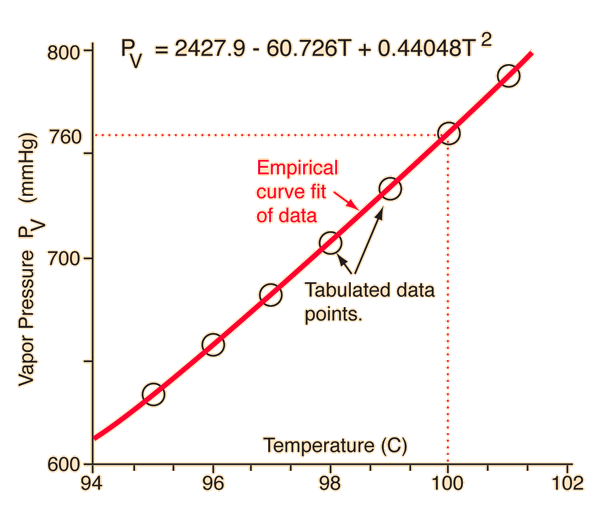
The vapor pressure of the pure solvent p o solv. This example problem demonstrates how to use raoults lawto calculate the change in vapor pressure by adding a strong electrolyte to a solvent. Antoinepressure 10a b c temperature the temperature t is expressed in degrees celsius and the vapor pressure p is in mmhg.