How To Calculate Surface Area To Volume Ratio Of A Cell
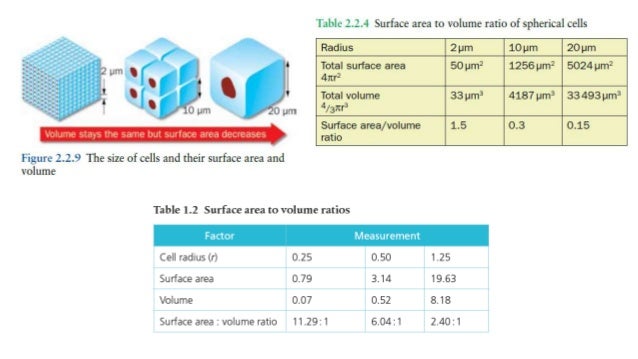
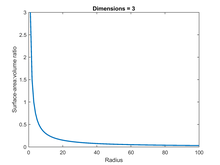
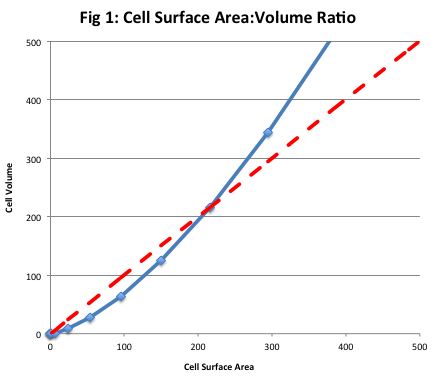
As the volume of the cell increases so does the surface area however not to the same extent.
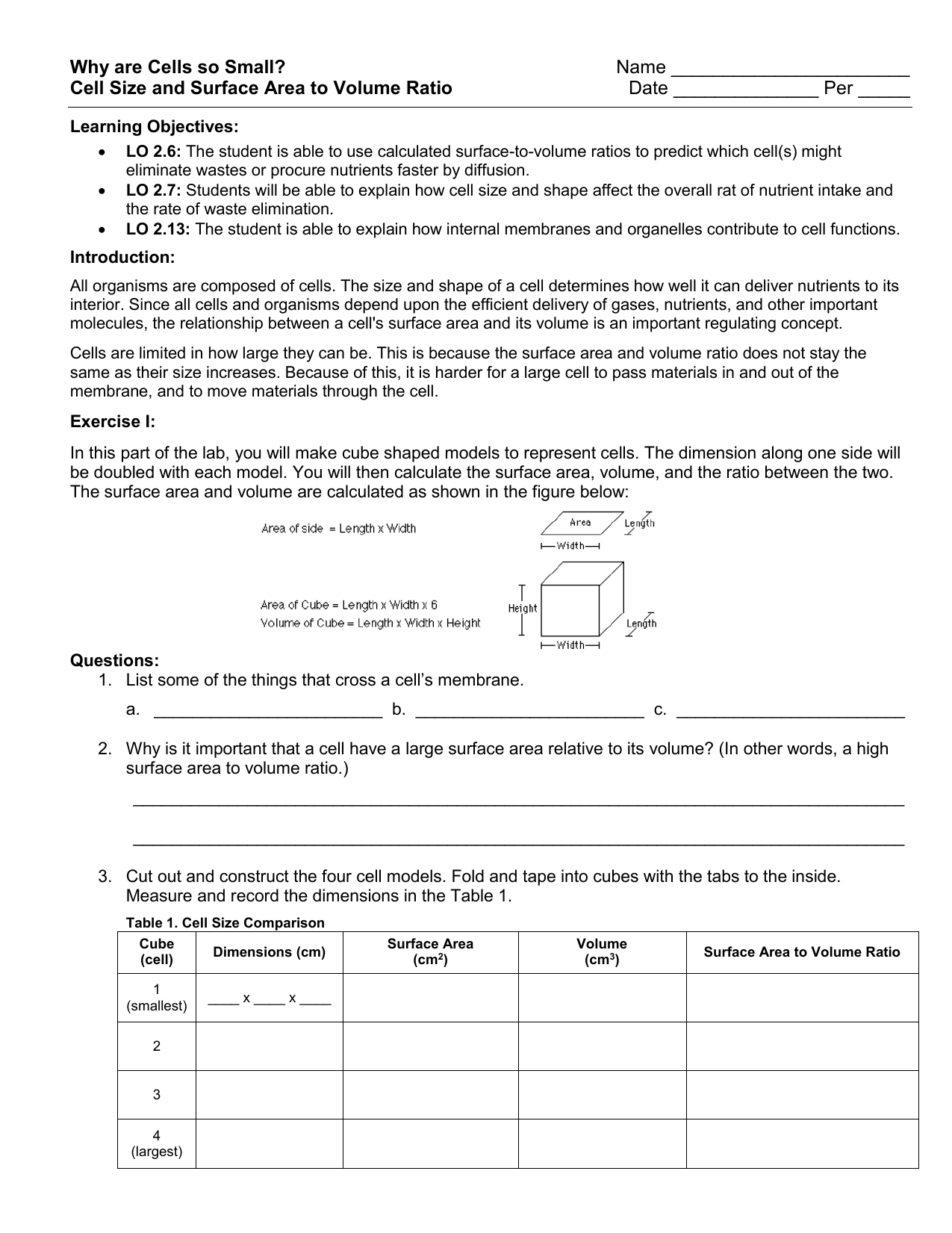
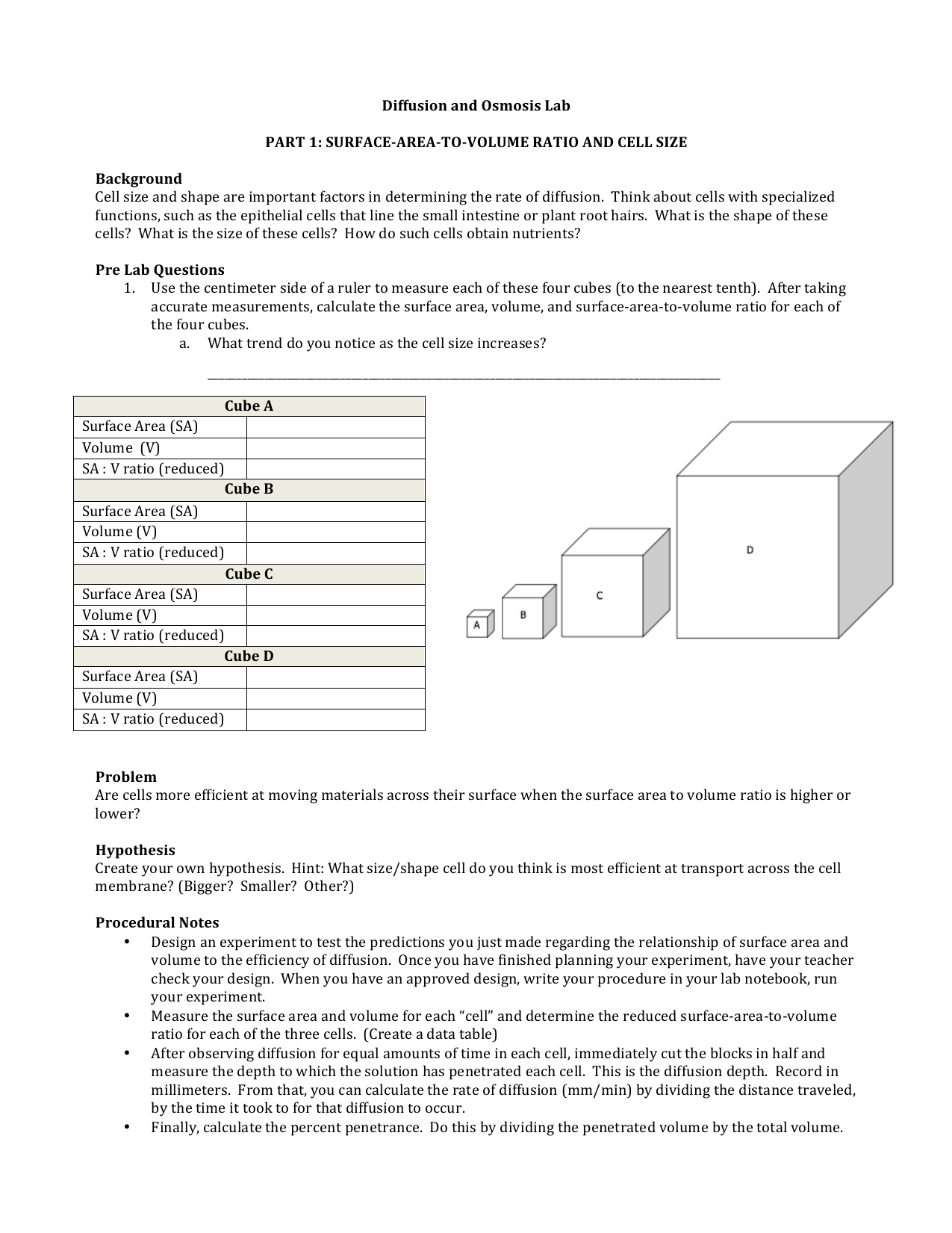
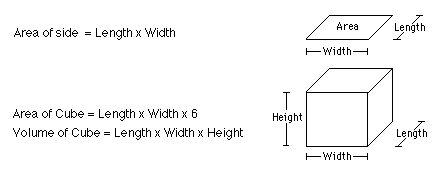
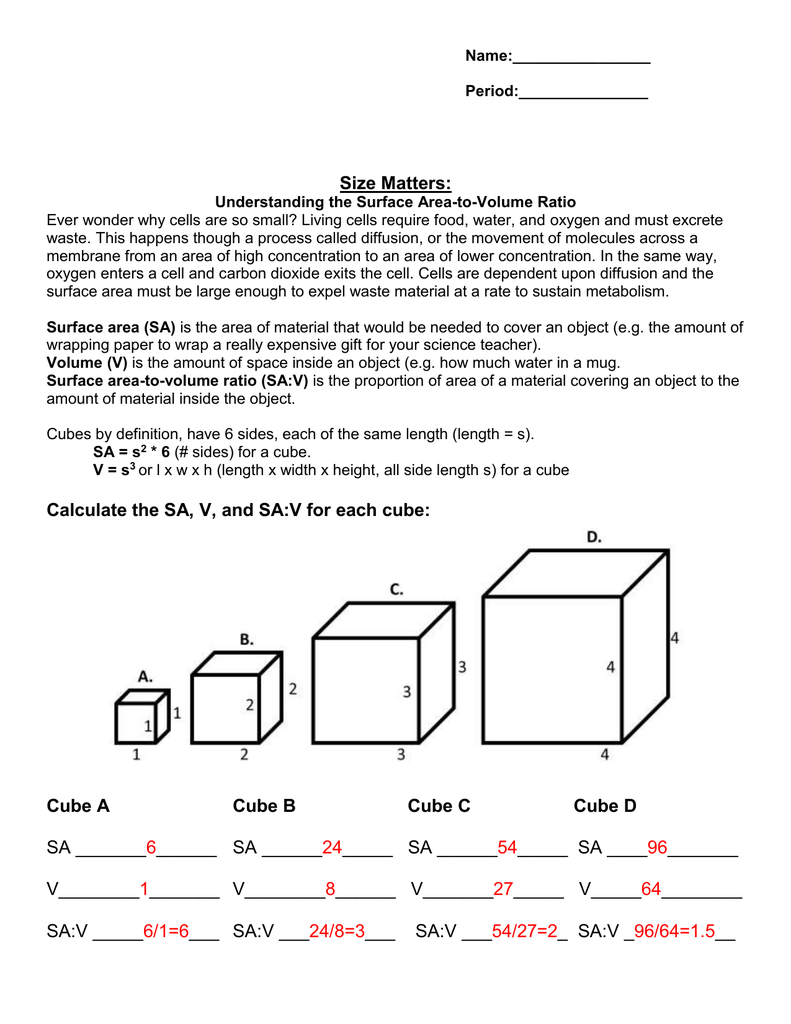
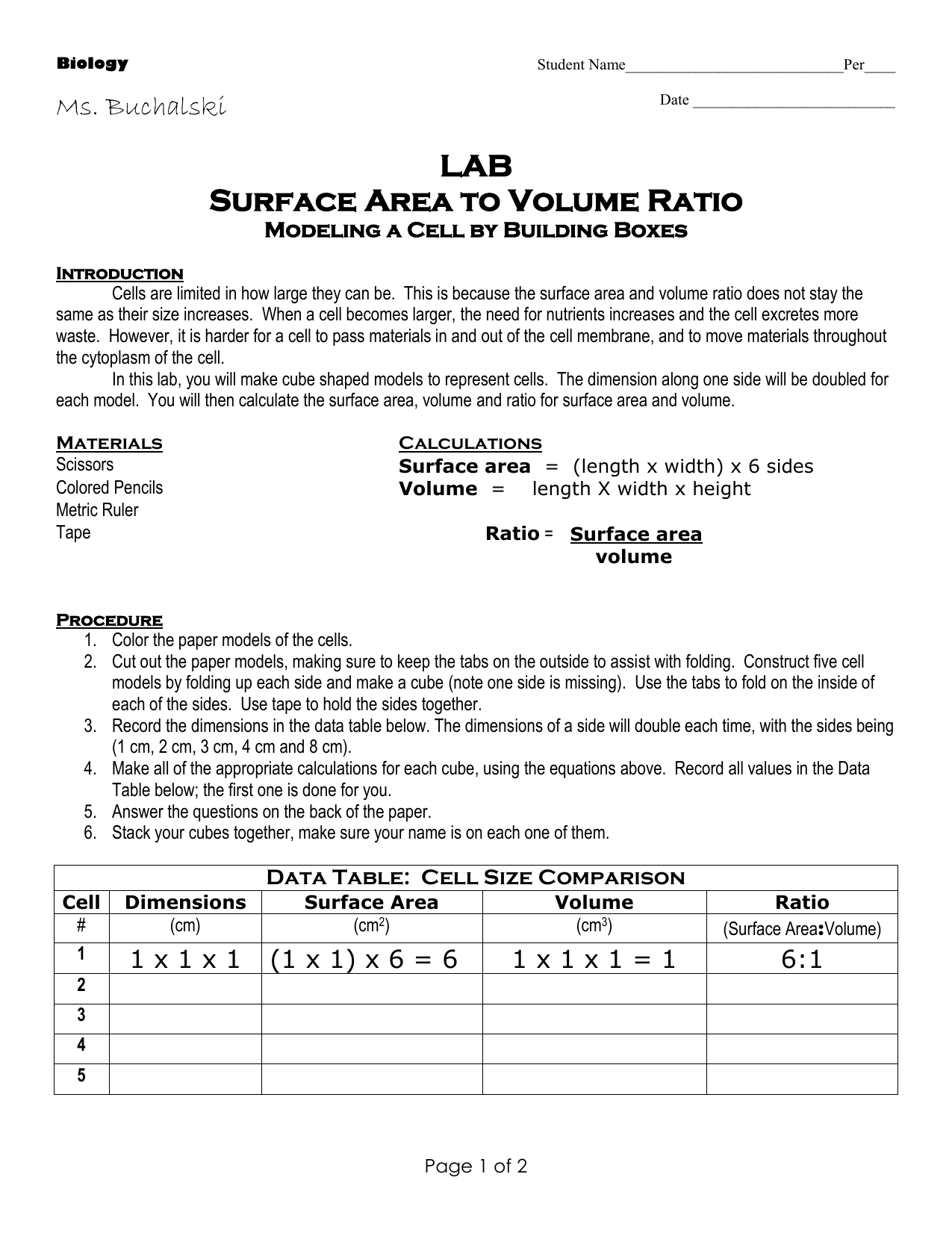
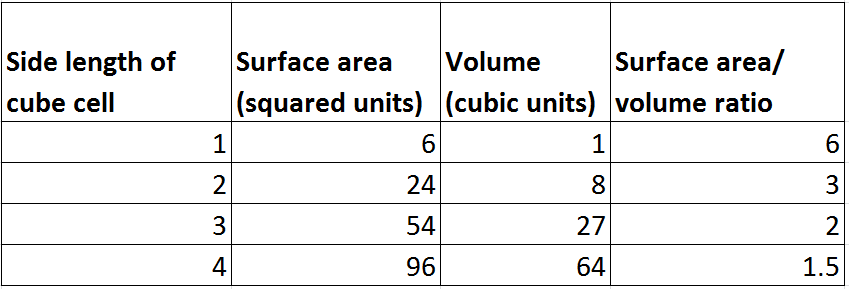
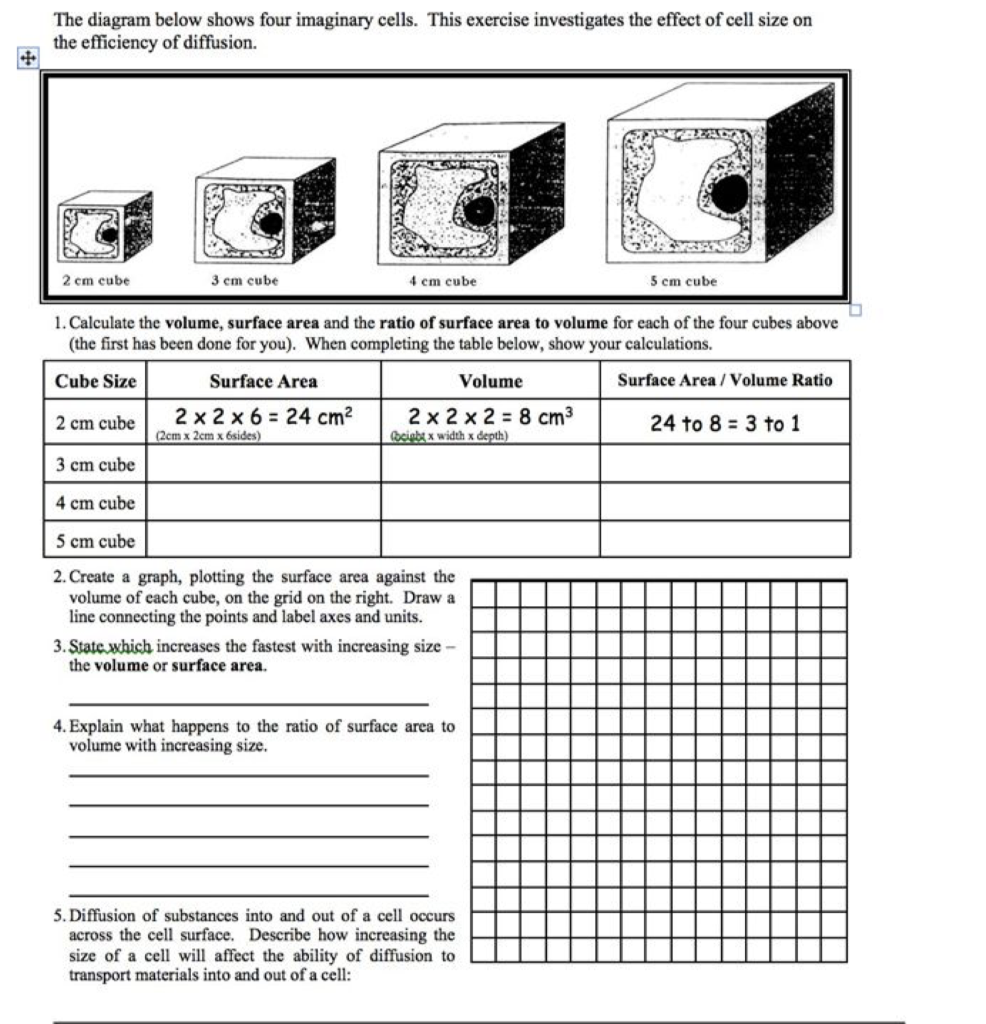
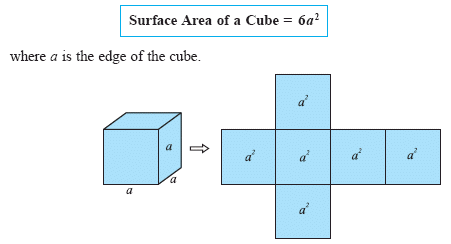
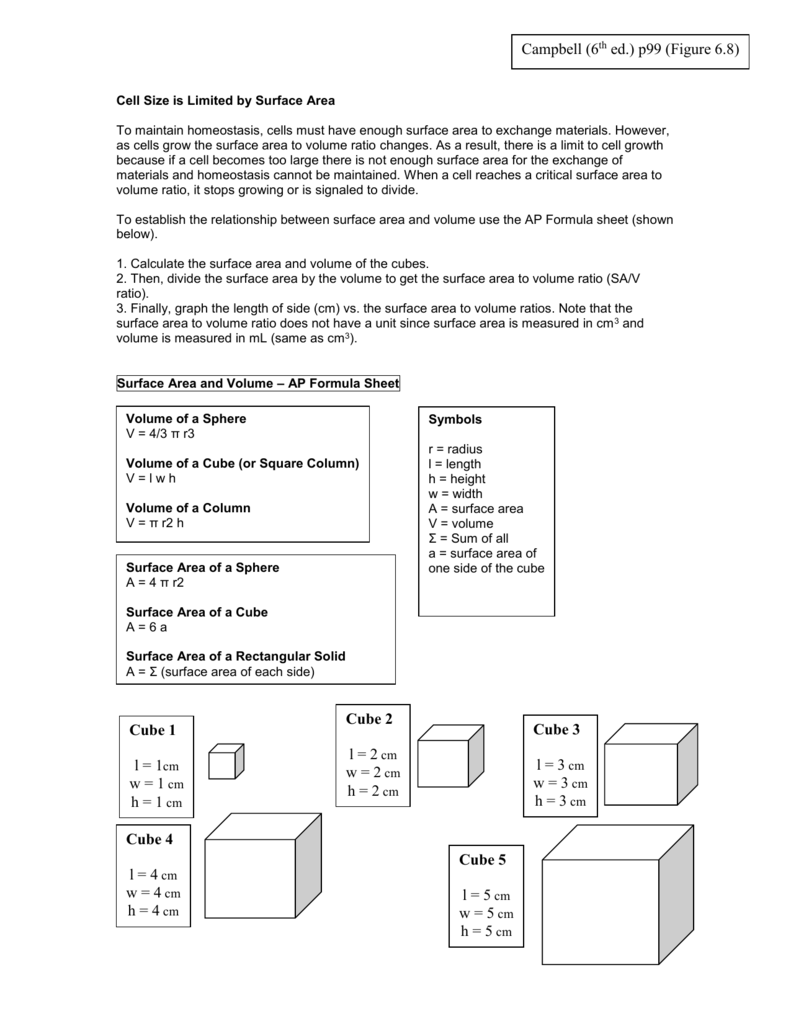
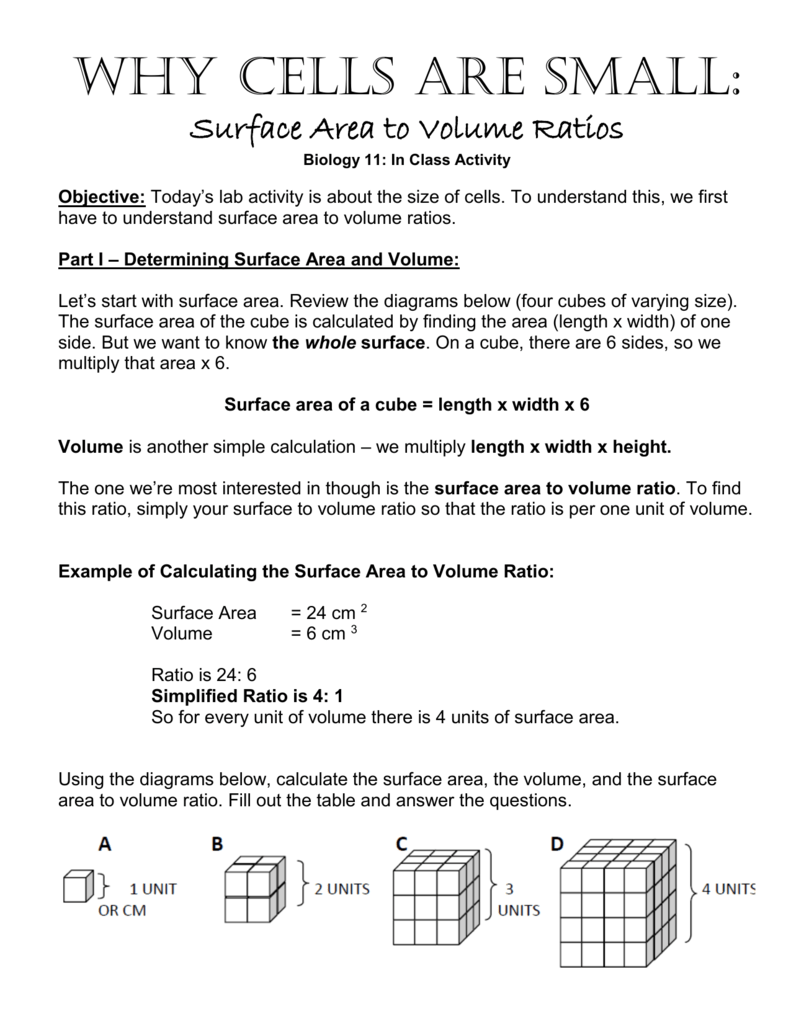
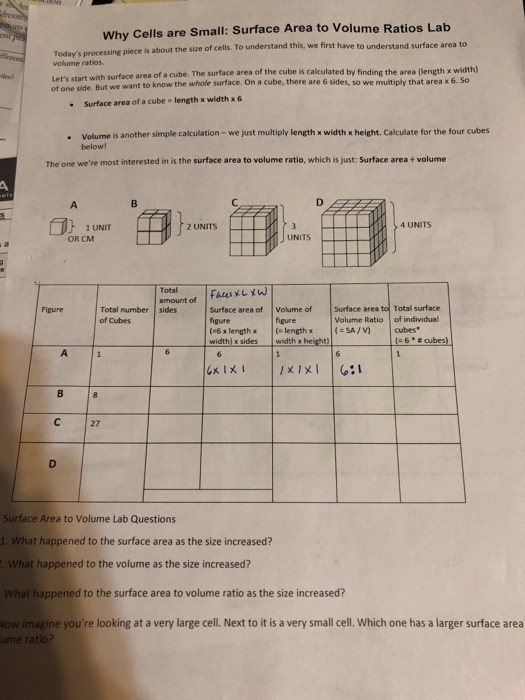
How to calculate surface area to volume ratio of a cell. The surface area of the cube is the area of each side x2 times the number of sides 6. Calculate what would happen to the surface area to volume ratio as the cell grows. Surface area to volume ratio of a cell. Calculate what would happen to the surface area to volume ratio asthe cell grows.
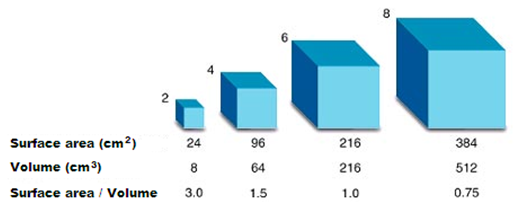
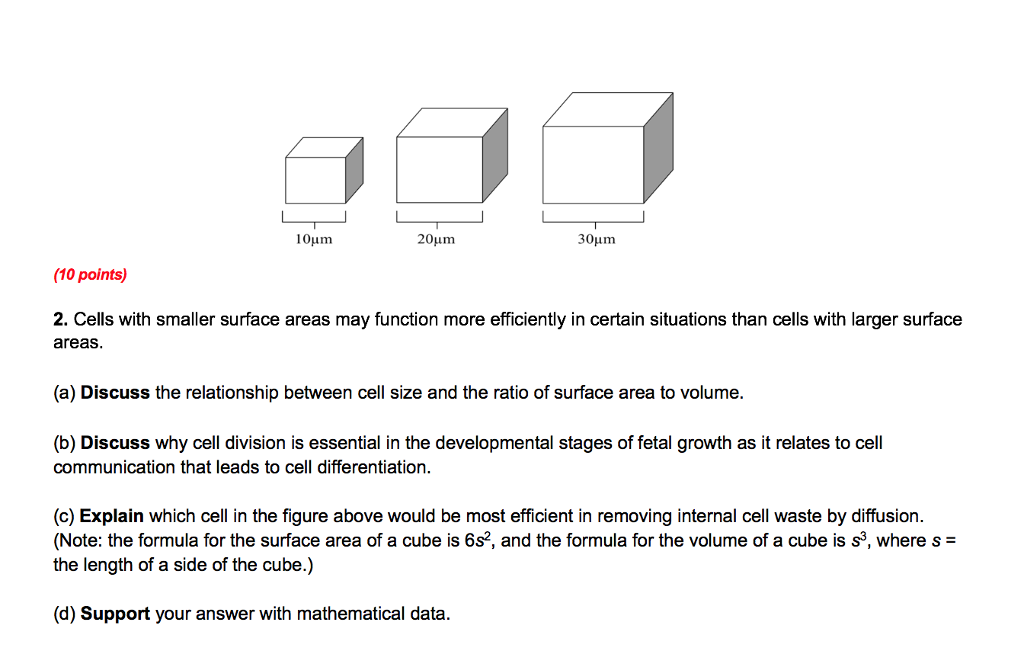
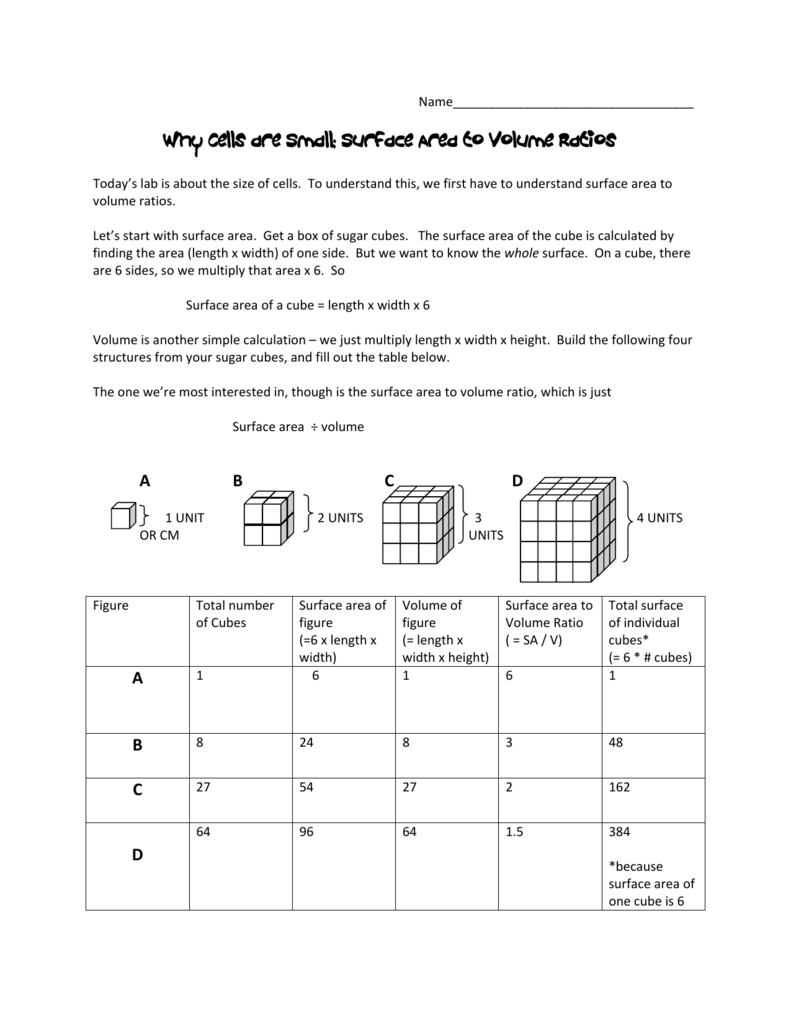
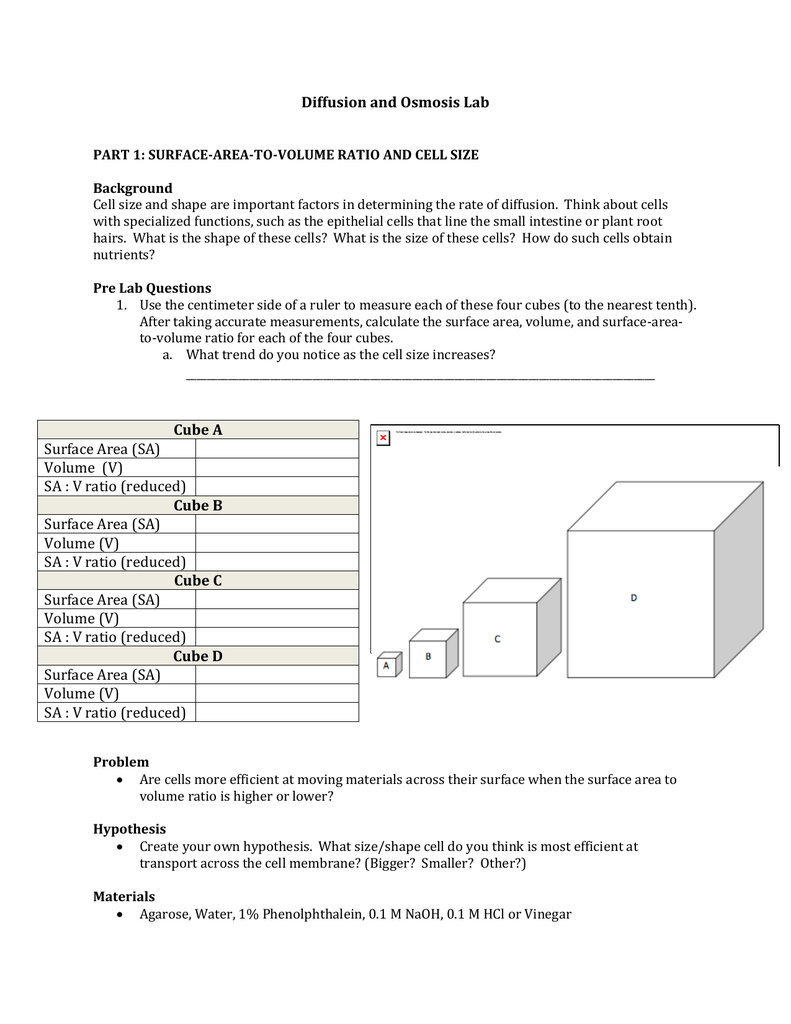
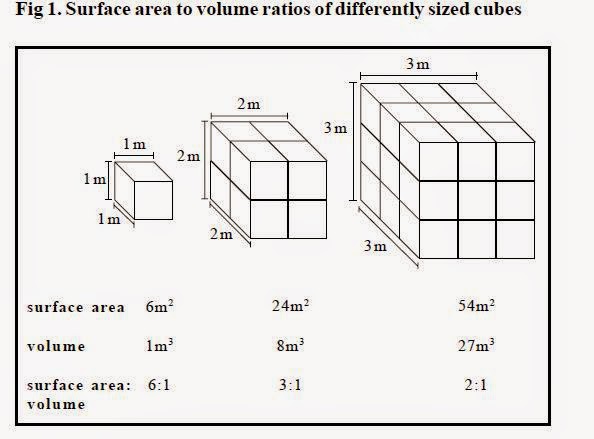
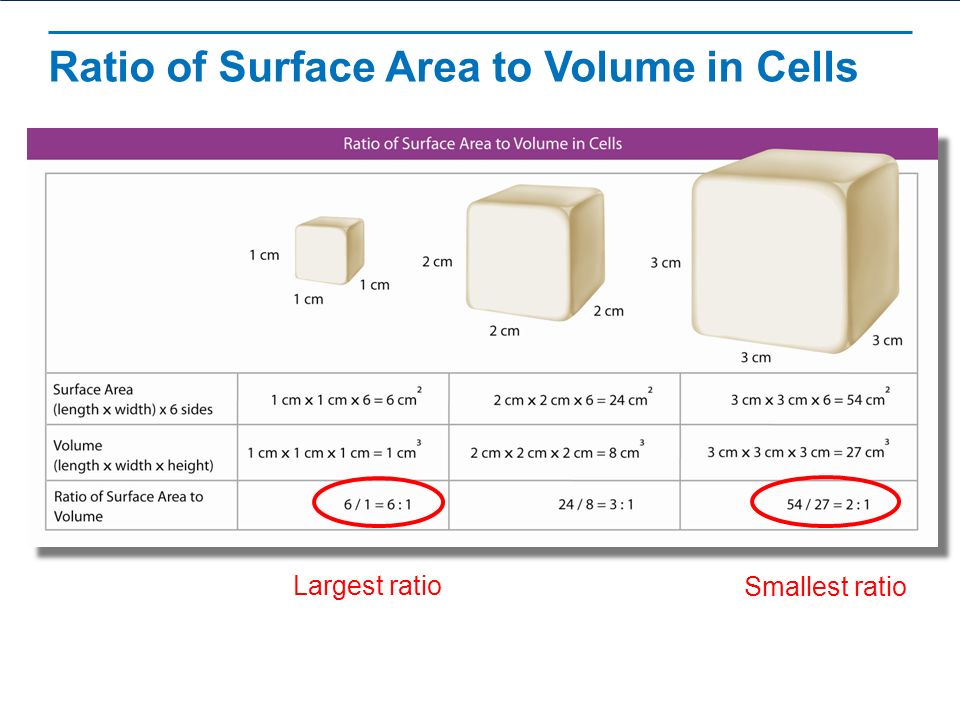
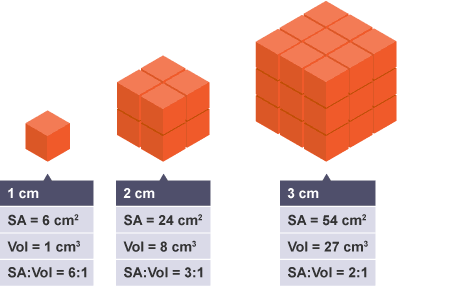
The surface area to volume ratio sav limits cell size because the bigger the cell gets the less surface area it has for its size. To illustrate this we can use three different cubes. The bigger your denominator the lower the value is going to be. The surface area of the cube is the area of each side x2 times the number of sides 6.
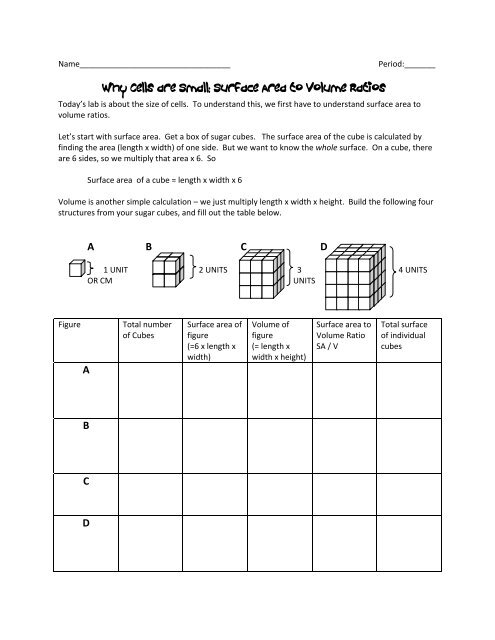
X the surface area to volume ratio for the above cube is equal to 21. Some of the worksheets for this concept are calculating surface area to volume ratios surface area to volume surface area to volume ratio volume and surface area work surface to volume ratios in plants surface area to volume cloze work chapter 2 structure. The first cube has a side of 1 cm the second 3 cm and the third 4 cm. Surface area to volume ratio of a cell displaying top 8 worksheets found for this concept.
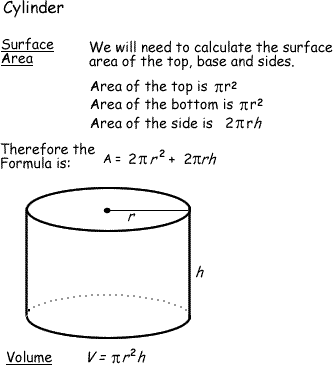
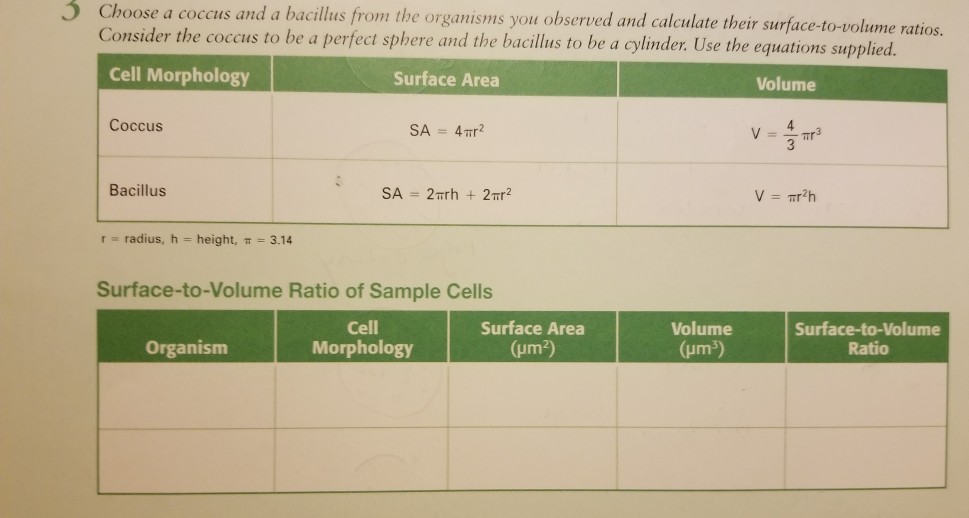
You could consider the cell to be a sphere and them just calculate it if you know the radius caluculate it like this 4pir243pir3 with r the radius of the cell the next question. And so what that tells us is is that as the volume of our cell increases as our cell gets bigger and bigger and bigger we have less surface area per unit of volume. The volume of the cube is x3. The volume of the cube is x3.
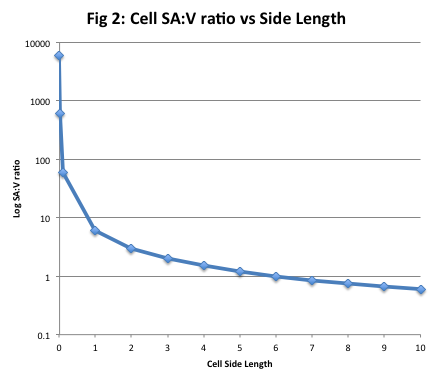
Since we are assuming the cell to be cube shaped allsides are equal so xlengthwidthheight. When the cell gets bigger its surface area to volume ratio gets smaller. Since we are assuming the cell to be cube shaped all sides are equal so xlengthwidthheight. That is for every 2 units of surface area covering the outside of the cube there is 1 unit of volume in the inside of the cube.
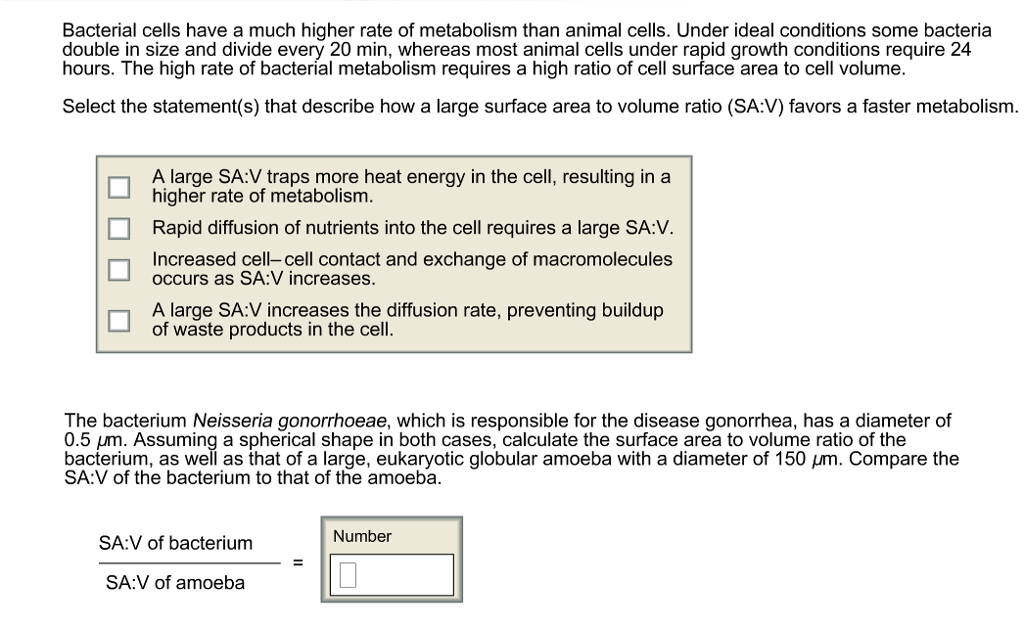
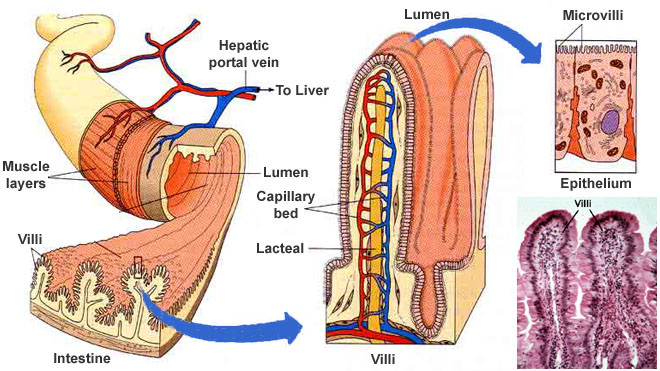
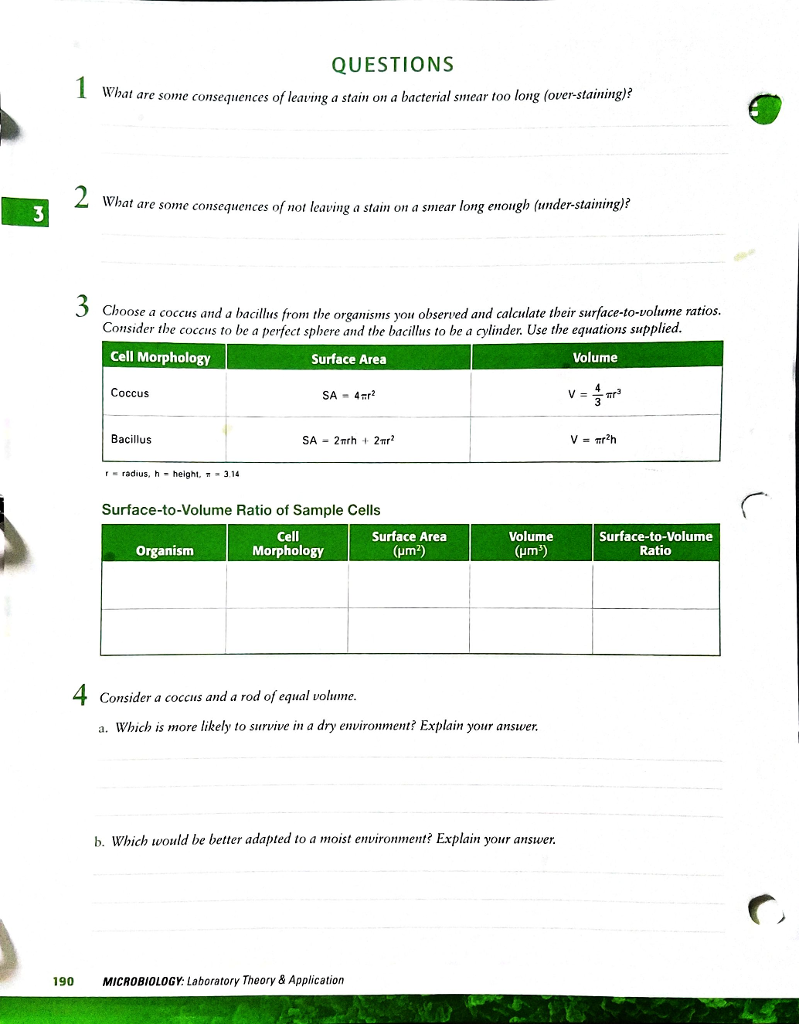
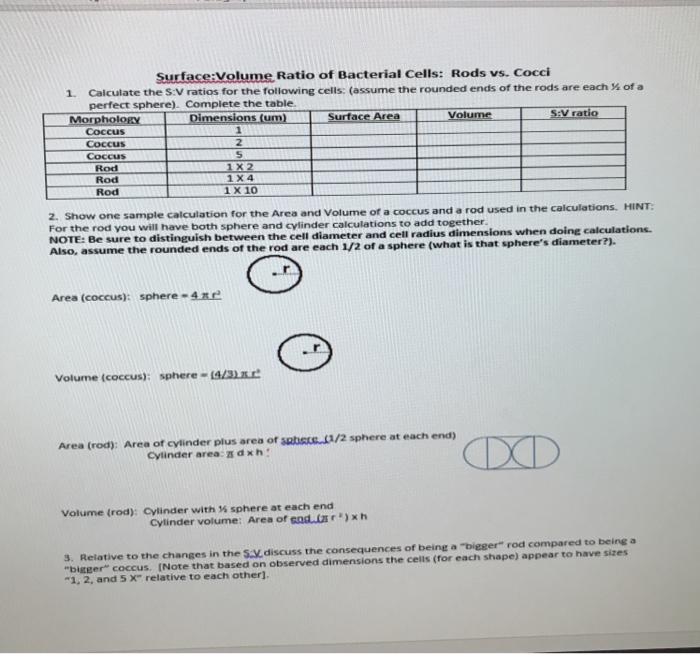
If we calculate the surface area to volume ratio we get. This is important if you are a cell that depends on diffusion through your cell wall to obtain oxygen water and food and get rid of carbon dioxide and waste materials. Most cells are spherical in suspension.