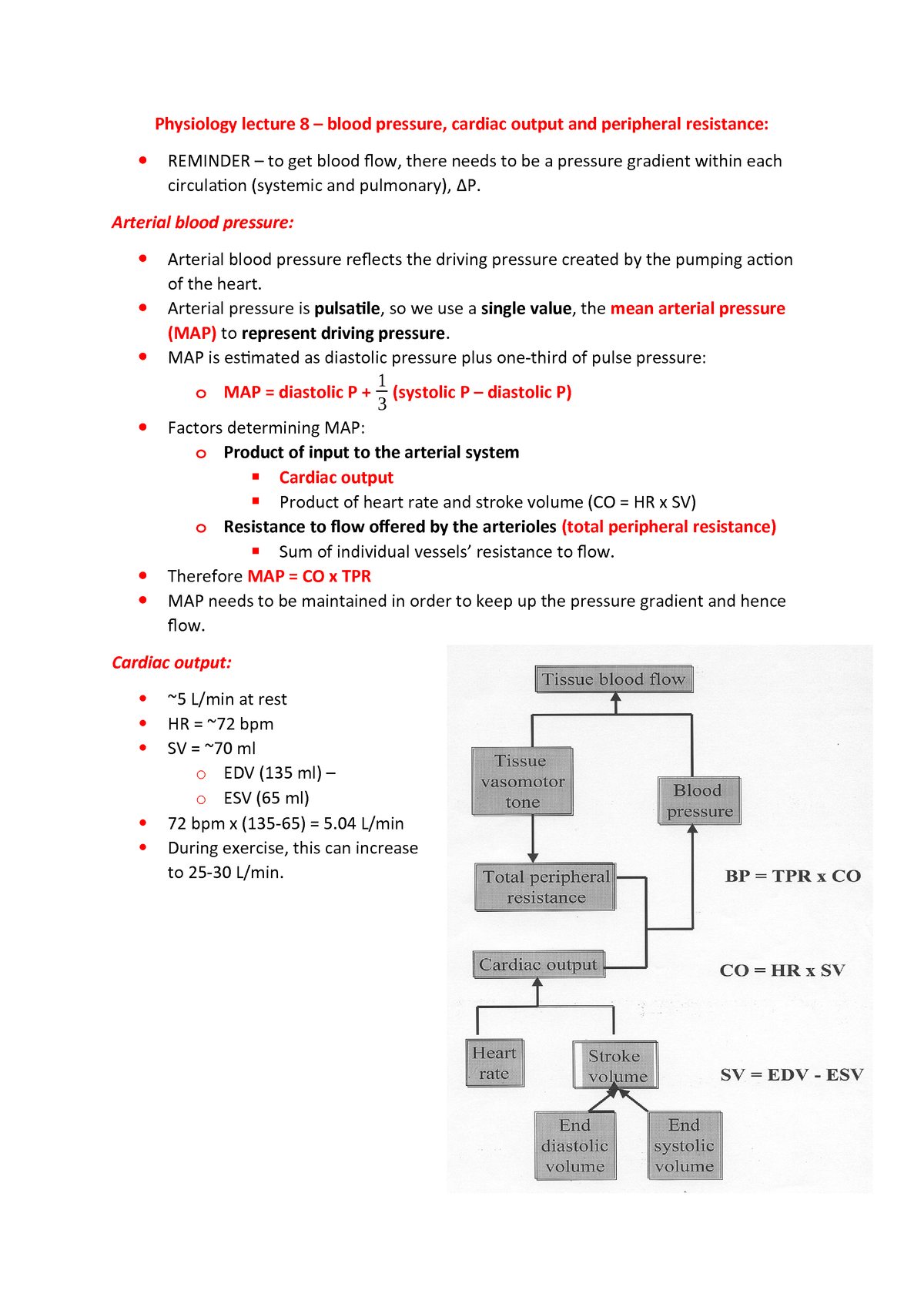
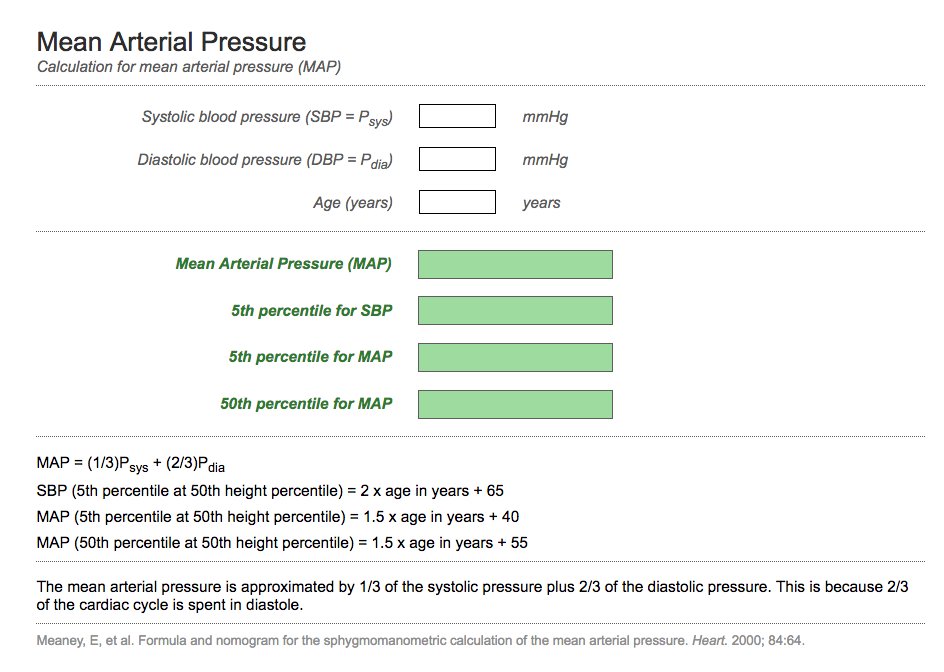
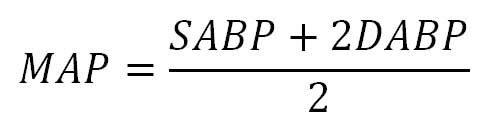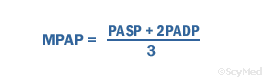How To Calculate Mean Blood Pressure
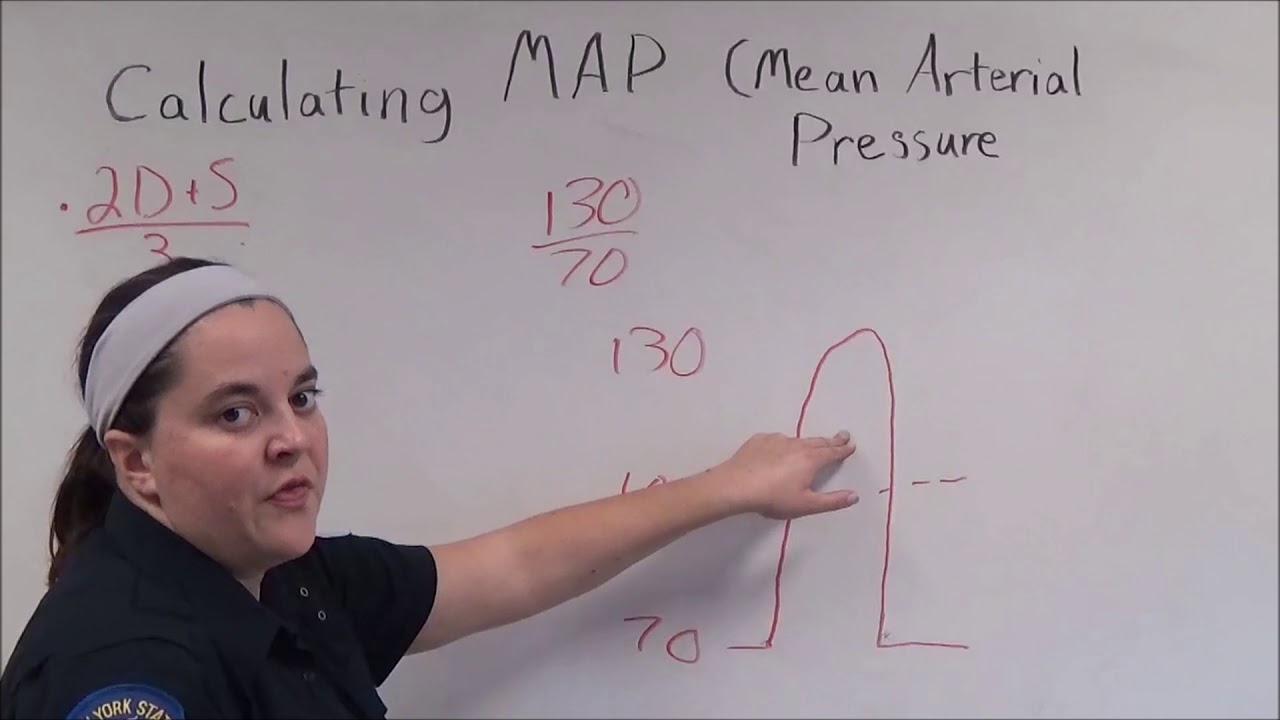
Alternatively use the formula map 13.

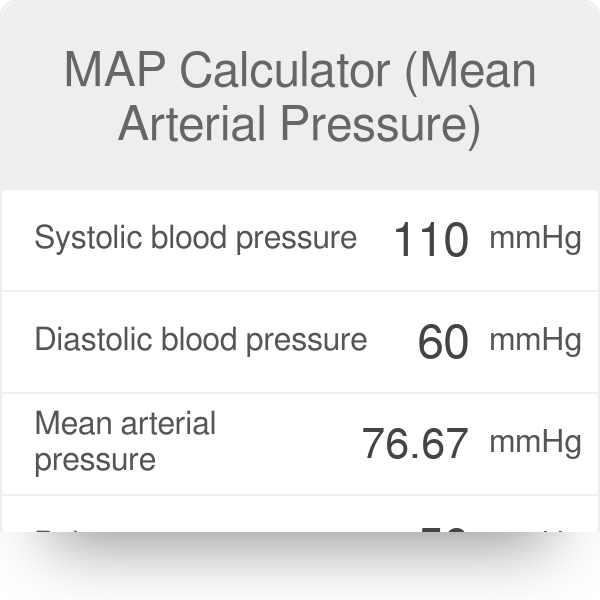
How to calculate mean blood pressure. You will also receive the status of your blood pressure according to this reading. Use the formula map 2 dbp sbp3. Map 2dp sp3. For example if a patients blood pressure is 83 mm hg50 mm hg his map would be 61 mm hg.
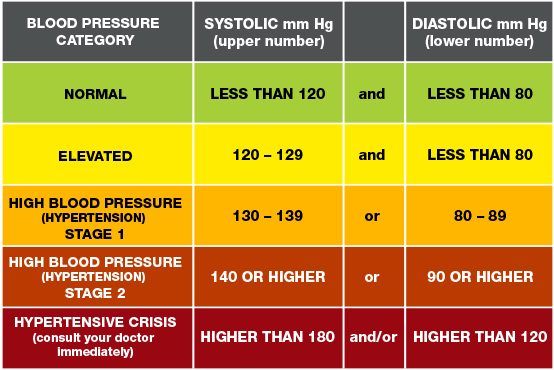
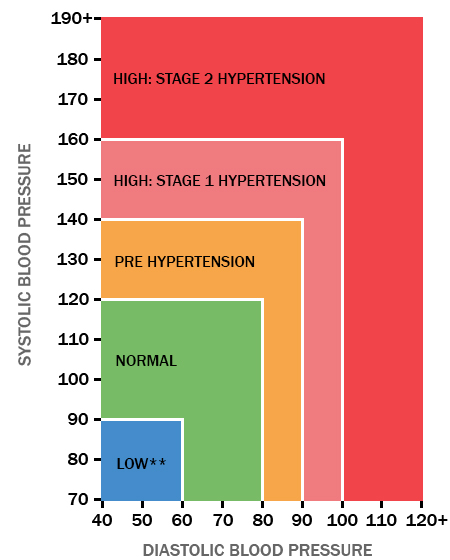
In general a normal blood pressure is considered anything less than 12080. To be able to calculate your mean arterial pressure youll need to know both your. The mean arterial pressure map formula used by the blood pressure calculator is. Then divide by 3.
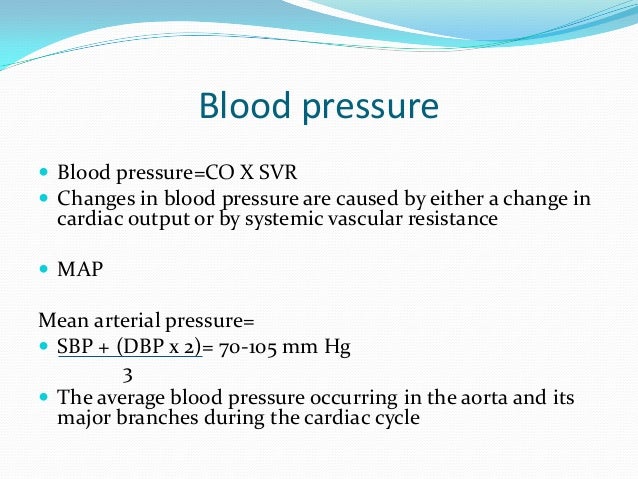
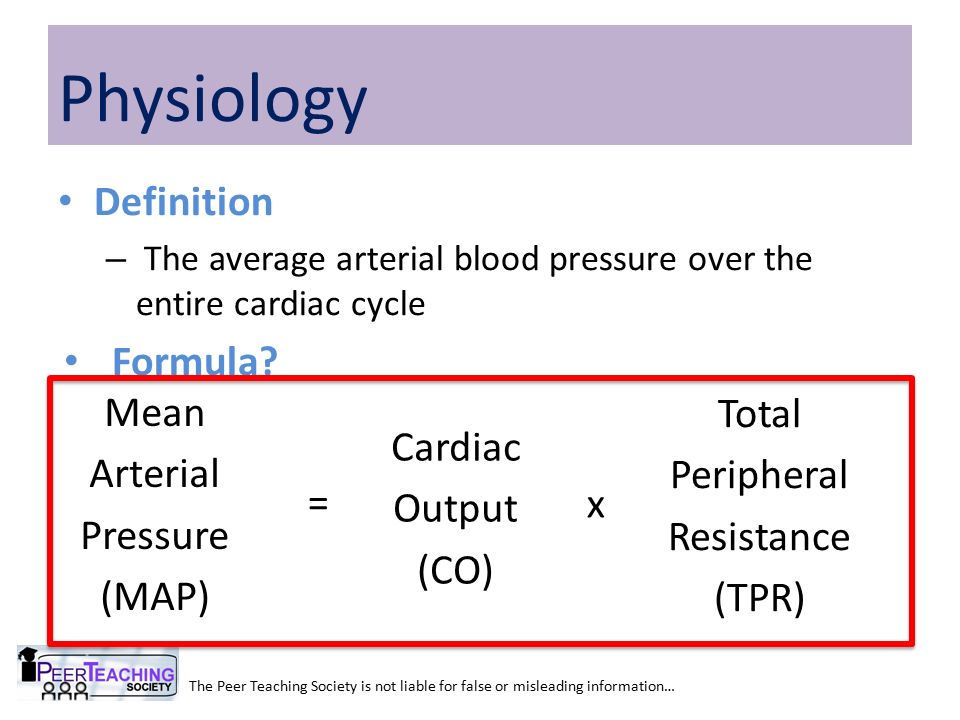
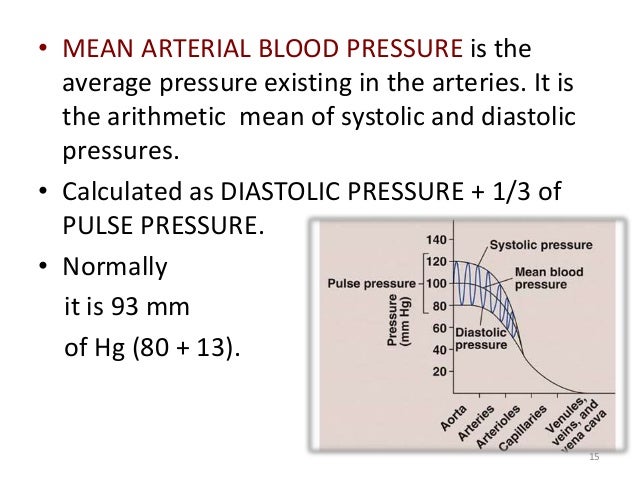
Pp sp dp. Mean arterial pressure to calculate a mean arterial pressure double the diastolic blood pressure and add the sum to the systolic blood pressure. The pulse pressure pp formula used is. Map sbp 2 dbp.
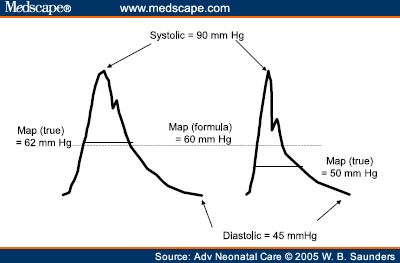
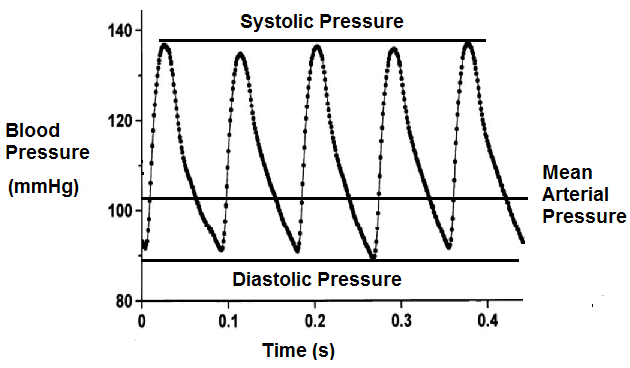
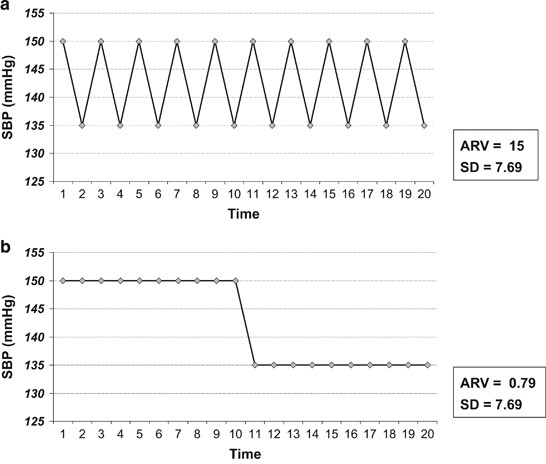
If you miss one or more of the readings do not write anything in the corresponding box. Step 2 total up each line. Here are the steps for this calculation. Note that map is based largely on dbp because most of the cardiac cycle is spent in diastole.
Input these numbers to the map equation. The normal map is 70100 mm hg and a map of at least 60 mm hg is necessary for adequate cerebral perfusion. The calculator returns the blood pressure status reading based on the following ranges for sp and dp. Find the dbp diastolic blood pressure.
Both high and low maps can indicate underlying problems such as internal bleeding. Step 1 enter your blood pressure readings fill out the chart by entering all of your readings 2 in the morning and 2 in the evening. It is the second number here equal to 80 mmhg. Once you know your diastolic and systolic blood pressures finding your map.
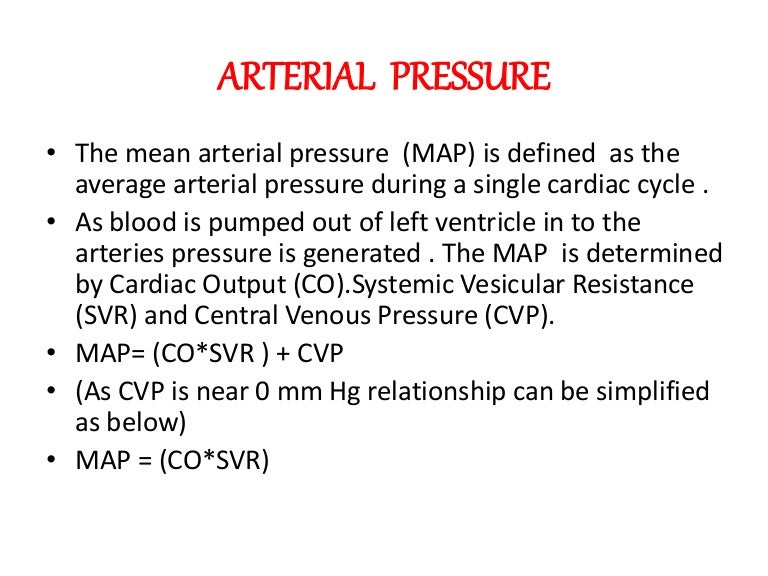
Using map formulas 1. Map sbp 2 dbp3. Take your blood pressure. The mean arterial pressure map calculates mean arterial pressure from measured systolic and diastolic blood pressure values.
Your own personal blood pressure will depend on your gender age weight and any medical conditions you have. Mean arterial pressure map measures the flow resistance and pressure in your arteries during one heartbeat.
















.jpg)